
Бесплатный фрагмент - Digital transformation for chiefs and owners. Volume 3. Cybersecurity
Foreword
Hello, dear reader. This is the final book on digitalization and digital transformation. In the first book, we looked at what digitalization and digital transformation are, why they are needed, what is the difference, what are the pitfalls. In the second they were introduced to the system approach, which is applicable not only for digital transformation, but also in general for any business. The system approach combines proven tools and digitalization, is accessible to anyone and aims to increase the impact of digital technologies, as well as to minimize the risks associated with the organization of work. At the same time, in the first part we talked that in the role model for digital transformation a specialist in information security is needed. Additionally, this is the direction I decided to devote a separate book.
It would seem that digitalization and cyber-free are incompatible, but it is impossible to continue digitalizing without befriending them. Recently at Denis Batrankov I have met a good definition of why it is necessary to deal with information security now: Previously, security was built on the story of the shark: you do not need to be ahead of everyone floating from it — enough to be ahead of the latter. However, now, when you are the target of the shark — it is more difficult to defend”. Additionally, this definition very accurately describes the current situation, as every year hackers’ attacks become more targeted. Additionally, 2022 in general became a landmark.
This book would not have been without the research of Positive Technology (hereinafter — PT), which became my first guides to the world of cybersecurity. Additionally, if you like to immerse yourself thoroughly in the primary sources, details, I recommend you study these studies. QR codes and links to them will be at the end of the book.
The book consists of three parts. The first is devoted to the review and analysis of the current situation. There will be many numbers, statistics, analysts, money. The task of the first part — to form your awareness of the problem and the understanding that information security (hereinafter — IS) — is a direction as strategic as all digitalization, and it is worthy of your attention. The main thesis is at once — a bottleneck in security, as in all digitalization — processes and people, not only yours, but also in the team of software developers (further — software).
The second part deals with the integration of information security from a systems perspective.
Well, the third part is devoted to practical recommendations on what to do here and now, how to choose IT solutions for information security, what people need to know and what competencies are needed.
If you’ve read previous books, you already know my approach — to control someone and delegate tasks, to trust your team, you need at least a basic understanding of its work. And the key task of the whole book is to give you the basic knowledge to build effective work with your team and the IS Director (hereinafter — CISO) with the least labor and risk for you.
Additionally, to avoid any misunderstanding, let’s look at the difference between information security and cybersecurity?
Information security is an activity that involves the prevention of unauthorized access, use, disclosure, distortion, modification, research, recording or destruction of information.
Cyber security is all the same, only related to IT systems and computers.
Part 1. Why deal with information and cybersecurity?
Chapter 1. Immersion and About Money
In 2023, it is already obvious that without the use of digital technologies it is impossible to conduct business, live comfortably, and manage the state.
If we talk about public services, public services in the form of online services are developing around the world. Russia is among the world’s leaders. I, for example, I use the state’s digital services to record a child to a doctor, and to view his vaccinations with test results, and to pay fines, taxes, tax returns.
If we talk about the commercial sector, it can no longer without online: payment for goods, booking tickets, receiving services, consultations, the appearance of digital advisers.
In general, digitalization and automation everywhere. Additionally, if you ignore them, you will be simply uncompetitive. Additionally, if you want to understand what is waiting for us in about 5—10 years, I recommend reading the observations of Yevgeny Bazhov about what is happening in China, in his book Made in China. How to conduct online business in Chinese”.
Let us also, for example, touch on the work with personnel. Without cloud technology and hybrid / remote operation, it will be much more difficult for you to attract talented employees and/or you will significantly overpay for them. Yes, the labor market is changing, of course, and now again the employer is starting to dictate its terms to the average worker. However, this is about the average worker. Additionally, if you want to attract talent, removing is a powerful advantage. According to my personal observations the removal/hybrid saves up to 30—40% on the wage fund. Young, flexible, hungry to the success of the company are actively using it. Additionally, one of the tendencies I see in job openings is that people who want to pay less just give you the opportunity to work remotely. Of course, I do not keep detailed statistics on the closing dates of these vacancies, but they close quickly. It seems even faster than companies with higher salaries, but the requirement to be present at the office daily.
It would seem that this is happiness — digitalization. However, where there are opportunities, there are risks. For example, the development of removals in the year 2020 led to an increase in hacking messengers and collective conference systems. Okay, well, if we could just plug in and crash the online meetings, but the hackers have a different tactic — they copy confidential meeting and chat records to go after extortion. Another modern trend is the encryption of internal files for ransom.
It is also necessary to look at the small developers of IT products: they themselves may not be of interest to anyone, but they may be attacked in order to build into their product malware, and through it attack a large company. Additionally, you can realize such a scenario without even attacking the IT infrastructure — you just need to recruit a remote employee who will make the necessary changes to the code. This approach, when large companies are attacked through contractors and suppliers, is called “supply chain attack”. This is another of the main trends since 2021. In 2022, up to 30% of targeted attacks were on this tactic.
The risks are added by the increase in the complexity of IT solutions, and the decrease in the qualification of the average developer, because the cheaper the developer, the more profitable everything from the point of view of economics. Competition and the market want complex solutions at a minimum price, which obliges to look for ways to reduce the cost of the product. However, all of this leads to an increase in the number of holes in IT solutions. Additionally, you’re not only facing direct financial and legal risks associated with penalties from suppliers and government and criminal liability, but also reputational damage. And if you go public, it’s also the downside risks of capitalization.
The most striking example of this is the attack on SolarWinds. Their clients were US government agencies and over 400 major American companies. Hackers embedded the virus in their solution and attacked their clients. The result is a 40% drop in the value of the shares in a few weeks.
If you look at the absolute numbers, from the beginning of 2017 to the end of 2022, the number of recorded attacks increased from 985 to 2921, that is, an increase of 196.5%. Here, of course, it is necessary to take into account the fact that we have learned better to detect attacks, but, looking ahead, I will say that even now 70% of the companies studied revealed viruses that were not known. The number of targeted attacks increased from 43% in 2017 to 67% in 2022. And although there were 73% of targeted attacks in 2021, the probability of targeted attacks is high. After all, 2022 is the year of the war in cyberspace, real and large-scale.
Now about money. The average ransom price that companies pay hackers is also rising. If previously limited to $1—2 thousand, now it is 4.35 million. The same applies to the maximum payout. In 2017, it amounted to $1 million, in 2022 — already more than 40 million.
The projections are also pessimistic. Therefore, Cybersecurity Ventures expects that the global cost of information attacks will increase by 15% and by 2025 will reach $10.5 trillion per year worldwide, with 6 trillion in 2021 and 3 trillion in 2015.
I will also give you a graph from PT on how the attacks change, who were attacked more often, and who are now in demand among hackers.
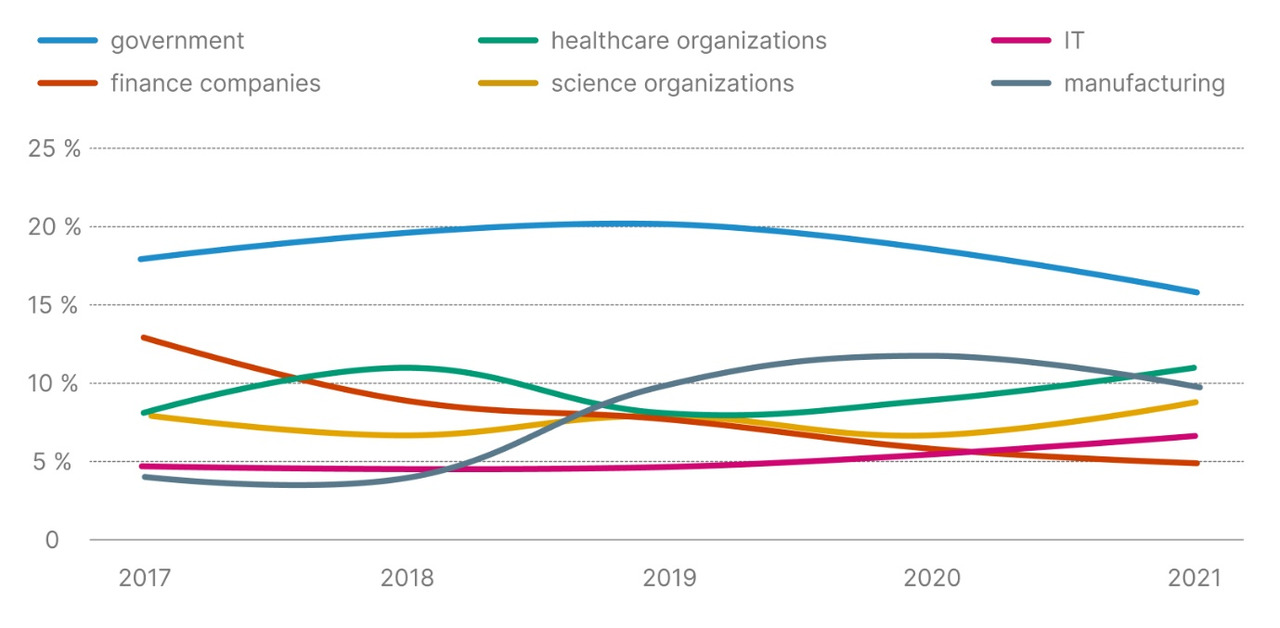
Here I recommend to pay attention to the financial companies — they are less and less interesting as they become more and more complex for attacks. In general, the market of “civil” hacking is more and more subject to the laws of business: intruders are looking for how to reduce the cost of each attack and increase its profitability. Therefore, hackers are looking for margins. However, this applies only to hackers who do not engage in political orders or targeted attacks, for example, from competitors. As a result, given that there is growth away from mass attacks to targeted ones, it is not necessary to rely on one economic expediency of the attack. If you order, you will be attacked. Especially if you are a Russian company. Additionally, if you are the first person, then it is you under the gun in the first place.
Chapter 2. On responsibility
Now the head of the organization is responsible for information security, which is reflected in the decree of the President of the Russian Federation V.V. Putin from 01.05.2022 250. Under its action fall federal executive authorities (federal ministries, services and agencies), management of subjects of the Russian Federation, state funds, state corporations and companies (for example, “Rosatom”, “Gazprom”, “Rushydro”, “RZD” and others) strategic and system-making enterprises, critical infrastructure facilities.
And while on April 20, 2020 the list of system-forming organizations included 646 legal entities, by July 2020 there were already about 1300, and in February 2022 — about 1400. However, you’d think if you weren’t on that list, why would you want it? It is necessary to understand that in our country, if you plan to grow, you will somehow start working with such organizations. This means that it is better to know the requirements of this document and be prepared. Overall, more than 500,000 organizations will fall under the new decree.
What is it recommended that organizations do under this decree?
— Establish personal responsibility for providing IS to the head of the organization, while allocating a separate Deputy General Director, who will have authority and resources to provide IS. It is either necessary to create a structural unit responsible for providing IS or to assign such functions to an existing unit.
— It is necessary to make an inventory of contracts with contractors providing IS services. Now such services can be provided only by companies that have a license to carry out activities on technical protection of confidential information from FSTEC Russia.
— Additionally, on March 30, 2022, restrictions were imposed on the acquisition of foreign equipment and software for subjects of critical information infrastructure (KIA), which make purchases for 223-FZ. Since January 1, 2025, organizations are prohibited from using information protection tools produced in unfriendly states, or organizations under their jurisdiction, directly or indirectly controlled by them or affiliated with them. There are 48 such countries in the spring of 2023. And even if the company supplying IS equipment, for example, from China, you still need to check its affiliates.
Going forward, I’ll make one guess. Taking into account all leaks and the importance of this topic for the state, you can expect the introduction of some insurance, following the example of the CTP. Each organization can be forced to insure against IS-risks. Additionally, then how the organization will build the IS function will influence the size of its premium.
Chapter 3. About General Trends
The main trend in the field of IS — professional managers come to the industry. Those who used to be engaged in “technology”, but now have grown up to managers. They think about the technical side of the issue, as well as about money, the processes in the organization, about the responsibility that they take on themselves. Additionally, this is a serious challenge for IS companies. After all, they need to communicate not just with experts who are in the topic, but find a common language with managers. That is to explain primarily in the language of money and guarantees.
The second trend — the transition from smeared protection throughout the organization, promotion of maturity levels and the use of best practices to a model of guaranteed protection against unacceptable scenarios: disruption of technological cycles, theft of money, confidential information, data encryption. That is, the transition from IS 1.0 to IS 2.0.
This is because everyone is already aware of the impossibility of protection from everything. First, the growth of digitalization and automation has led to an increase in the number of software used. Which means there’s an exponential increase in the number of attacks. Secondly, as we have said before, all IT solution developers try to reduce costs. For example, even the world IT giant IBM transfers its production to India, because there is cheaper labor programmers. At the same time, the quality of the code from most Indian developers leaves much to be desired. It’s like Chinese replicas of original products. All this leads to a decline in software quality and an increase in the number and criticality of vulnerabilities.
Additionally, even published “holes” developers do not hurry to eliminate quickly. Here are indicative statistics from PT. Of all vulnerabilities in industrial IT systems identified and sent to developers in 2021, less than half — 47%. In this case, they become known to the world quite quickly — within a few hours.
In total, about 25,000 new vulnerabilities discovered by security researchers were identified and confirmed in 2022.
The increase in the number of startups and their programs, as well as the failure to comply with the principles of safe development, can lead to this number being only increased.
As a result, it turns out that in more than half of the attacks, hackers quietly use these vulnerabilities and get the necessary access in a few minutes. PT specialists themselves, using known vulnerabilities, were able to access the internal network of companies in 60% of their projects. Additionally, now add the fact that there aren’t many white hackers and researchers, and the developers just don’t know about all the holes. Hackers do not seek to publish found vulnerabilities in the public domain. At the same time, the shadow market of hackers itself is on the rise.
Third, attacks become targeted rather than mass attacks. As mentioned earlier, it was 43 per cent, now it is 70 per cent.
Fourth, no matter how advanced the technology, the bottleneck is still people. Therefore, since 2017, the number of people caught on phishing letters, not only has not decreased, but, on the contrary, has increased multiple. Additionally, in the top most used and effective ways to penetrate the company is still phishing via email. In this case, the topics that people open most often remain unchanged from year to year: salary, bonuses, social programs, DMS, resume. In addition, the best mailing lists dedicated to events in a particular company or division. That is, the growing role of social engineering.
The statistics of attacks against ordinary people are interesting. After all, the endless leaks of personal data make it easier for hackers to choose the right people when planning an attack on the organization. So, in 2021 in 58% of attacks hackers infected users’ devices with malicious software: these were applications for remote control (34%), spyware (32%) and bank trojans (32%). By the end of 2022, spyware was already used in 49% of successful attacks.
At the end of 2022, phishing sites (42% of successful attacks) and emails (20%) were the most common source of infection. Hackers also combined people’s personal devices and organized so-called ddos attacks, that is, simply overloaded the IT infrastructure of the victim organization. Additionally, in massive phishing attacks hackers used the current news agenda: purchase of fake certificates of vaccination, creation of fraudulent sites before the European Football Championship, premiere of a new episode of the series “Friends” or other “delicious” event.
Additionally, fifthly, managers are pragmatic people who want guarantees. As a result, we came to the second trend — the formulation of simple and understandable for top managers queries, so that the unacceptable could not be implemented.
In my opinion, this is quite a normal situation. It is impossible to build up armor indefinitely and close. If you like to drive tanks, remember the example of the Mouse tank, which eventually became sluggish and in life could not move at all, becoming only a museum exhibit. At the same time, the development of technology still made it pierced. In the struggle of armor and projectile always in the end wins the projectile.
Returning to the language of business, I will share an observation. Increasing the armor sometimes leads to the growth of useless bureaucracy. I’ve seen companies close so that business processes stop, and people just go outside the company, start working communication and document exchange in open messengers and personal mail. After all, they have KPI and they require results. And waiting for a week or two until the technical support solves another problem, they cannot. In the end, we want to defend ourselves, but only by multiplying the risks.
The third trend is the development of cyber-polygons and cyber-battles, which provide an opportunity for cyberbes professionals to try their hand at detecting and suppressing malefactors, testing infrastructure and obtaining information for analysis and development. Additionally, since the beginning of 2023, there is active creation of programs to search for vulnerabilities for reward. Such programs are called Bug bounty. This allows “white” hackers and researchers to apply their knowledge for the good and get a reward for it. This applies mainly to the financial sphere (vulnerability search programs) and large corporations (participation in cyber battles).
Chapter 4. What happens in the Industry
Attacks on corporations and organizations are becoming increasingly like planned military operations — attacks on both equipment and people. Therefore, we already know about phishing, exploiting vulnerabilities and so on. However, in addition, there are specialized companies that are developing tools to penetrate various information systems. This is particularly the case in countries where such work is not restricted by legislation. That is, in principle, it is not an illegal business, and given the current situation, many countries are likely to turn a blind eye to it altogether.
Public administration and organizations
State organizations now, in 2022—2023, are undergoing a real combat baptism. In 2022, the number of successful attacks on government agencies increased in every quarter. Government agencies faced the highest number of incidents among any organization. They accounted for 17% of the total number of successful attacks (in 2021 this figure was 15%). In total, in 2022 PT recorded 403 incidents with state organizations, which is 25% more than in 2021.
The main way of attack is social engineering. The target of attacks is data. And this is understandable, because automation and digitalization into the state. Control is well under way. This means that public authorities are beginning to generate big data: taxes, medical information, biometrics, etc. Medical data are of special interest to hackers, including for the purposes of social engineering, increasing the effectiveness of phishing attacks.
The most popular types of malware were cryptographers (56%) and programs for remote control (29%). Additionally, the share of attacks on web resources is constantly growing — in 2020 there were 14%, by the end of 2022 — 41%.
Additionally, government structures are under attack not only in our country.
Example 1
In mid-October 2021, the hacker gained access to the Argentine government’s database, which contains information on all citizens’ identity cards. As a result, on the black-market data and ID-cards of the entire population of Argentina, that is, more than 45 million citizens were put on sale. Moreover, as a confirmation of the data, the hacker disclosed information about 44 known personalities, including the President of the country.
Example 2
Police Department of the US capital Washington. There was a massive leak of internal information after the attack of the extortion program. Thousands of confidential documents were published in the darkwebe (a segment of the Internet that is hidden from ordinary users, where people sell forged documents, weapons, drugs, and hackers orders). Hundreds of police files, informants and intelligence reports from other government agencies, including the FBI and the Secret Service, were also discovered.
Example 3
The hackers’ data encryption attack caused the collapse of the IT infrastructure of three hospitals in the United States, disrupted several routine surgeries, disrupted patient intake, and stole 1.5 TB of personal data, including medical records. The group received a $1.8 million ransom for decrypting the stolen information. A cyber-attack of extortionists on one of the main hospitals of Barcelona (Clinic de Barcelona) resulted in damage to the IT infrastructure of the clinic and forced to cancel 150 urgent operations and up to 3000 patient examinations (according to the Associated Press).
Example 4
Another interesting case was November 2022. At one of the forums in the darkeven there was a report about the hacking of the infrastructure of the Federal Tax Service of Russia. Hackers claimed to have downloaded 800 GB of confidential information. No official comments from the agency were received. The evidence included references to several projects, which according to hackers were taken from the NRF database. “It only took us a week to get into the IRS network, and only three people were involved in the hack. In fact, we have already captured several dozen state structures of this level. However, there is no need to claim them yet,” said the hackers in the message.
At the same time, another curious case with FTS occurred in 2019. Then it was possible to access two databases. The first contained more than 14 million data on people, and the second — 6 million. They included names, addresses, passport numbers, residence data, telephone numbers, TIN numbers, names of employers and information on taxes paid.
Example 5
An extortion attack on a Costa Rican government facility in April 2022. A group of extortionists, Conti, attacked Costa Rican institutions and demanded a $20 million ransom. Due to the inaccessibility of most of the country’s IT infrastructure, a state of emergency was declared, and later the attacked public sector was joined by Costa Rican health care, whose institutions were attacked by the Hive group.
Example 6
Burlington City, Canada, was the target of a phishing attack in which $503,000 was transferred to a cybercriminal rather than a real service provider.
Industry and energy
The industry is increasingly attracting cybercriminals: the number of attacks in 2021 exceeds the results of 2017 by more than 7 times. Additionally, in 2022, about 10 percent of all successful attacks came from industry. At the same time, industrial companies, in fact, are not ready to withstand complex attacks and malware. Thus, 95% of companies either do not protect their automated process control systems (ACS TP) special solutions, or do so partially. Additionally, a systematic approach to cybersecurity management, such as vulnerability management and software component upgrades, is also lacking in 93 percent of cases. This is in view of the fact that the damage from stopping business processes can be catastrophic, including with damage and destruction of equipment, man-made disasters. Companies are easier to follow hackers and pay ransom quietly.
What saves us now is that it is simply unprofitable for intruders to study technological parameters, to understand exactly what to change, because you can simply encrypt or steal confidential data. In my view, that is a key deterrent.
The general trend is also maintained here — the attacks are becoming more complex:
— using Malicious Software (71% Successful Attacks)
— social engineering (about 50%)
— exploitation of software vulnerabilities (41%).
Malware itself was distributed through IT equipment (49% of cases) and mail (43%). Interruptions to technological and business processes occurred in 47 per cent of cases. Additionally, mainly because of data encryption and data deletion software (vampers). During 2022, the share of ciphers increased from 53% in the first quarter to 80% in the third. The share of waxers reached 7% (in 2021 it was 1—2%).
The increasing share of vulnerability exploitation in attacks suggests that these methods are economically feasible, which already indicates a low level of protection in industry. And it was in software and hardware products designed for industry that the most dangerous vulnerabilities were discovered and corrected in 2021.
Industrialists and power engineers like and are aware of all risks, but the specificity of the industry does not allow to conduct full-scale exercises with the development of practical scenarios and the identification of unacceptable events. Therefore, there are now emerging cyber-test sites where you can use virtual or augmented environments without the risk of breaking processes and equipment, conducting any exercises and assessing the consequences. One such example is the Standoff event organized by PT.
In general, in 2021, the interests of hackers in Russia by branches of industry were distributed as follows:
— 31% aerospace industry;
— 23% of public organizations;
— 23% of IT-company;
— 15% Military Industrial Complex;
— 8% fuel and energy complex.
As for PT statistics, in their projects from the first half of 2020 to the second half of 2021 they managed to implement 87% of unacceptable events.
Finance
The financial sector is one of those who feel relatively well. The proportion of attacks on these organizations from the total number of attacks decreases from year to year. And most interestingly, there are no new groups seeking to withdraw money from banks. The reason for this is the maturity of the industry and the efforts of the Central Bank: regulations, investments in IT infrastructure and software, established information exchange. And this is understandable, if you steal money, you can see it here and now.
Organizations are attacked again through social engineering (47%) and the use of malware (downloaders, spyware, trojans, encryptors.
Theft of confidential information and stopping of key business processes (53% and 41% of cases respectively) were typical targets of bank attacks. Embezzlement was 6% successful.
Financial institutions are now under attack with the aim of:
— obtaining a better exchange rate;
— obtaining confidential information about the user and its use in other attacks by means of social engineering;
— increase system load and failures in users’ private offices.
In addition, there are still unsafe implementations of fast payment systems.
As a result, banks introduce all new security technologies:
— tighten the checks of KYC (mandatory verification of personal data of the client), including the development of services for checking documents (video calls with document recognition, downloading photos of documents, database checks, social activity assessment) to understand whether a real person is hiding behind an account;
— introduce machine learning systems to speed up, simplify and improve customer information retrieval, identify and block suspicious transactions.
As a result, the number of standard web vulnerabilities decreases, but the number of logical vulnerabilities, on the contrary, increases. And in many ways this is due to the development of ecosystems: the creation of more and more complex integrations, microservices, the introduction of voice assistants and chat bots.
However, there are two negative factors that allow PT specialists to find vulnerabilities in each organization that allow them to penetrate the internal IT infrastructure. First, security patches released by software developers are often ignored by the IT services of organizations and are not installed. Second, there is always a possibility of a vulnerability, which is still unknown to developers, but it was discovered by researchers of intruders. Such vulnerabilities are called “zero-bottom vulnerabilities”. Additionally, these factors are the key to getting the hacker inside the infrastructure, so you need to learn how to spot them in time.
In total, PT specialists were able to penetrate the internal network of organizations in 86% of cases. PT researchers also gained full control over the infrastructure and implemented unacceptable events: access to bank-critical systems, ARMA treasurers, money exchange servers. In total, PT experts managed to implement more than 70% of unacceptable events in each financial institution.
As a result, the extortionists will continue their attacks on the banks. So far, these attacks are easier to execute and cumulatively bring more profit than attempts to withdraw a large amount of money from accounts. However, now one of the main targets of hackers will be the clients of banks that use online banking. According to the Central Bank of Russia, in 2020, 75% of adults used online banking. Therefore, hackers will continue to develop the direction of compromising banking applications. Additionally, the techniques of social engineering will remain in use.
The main method is phishing — it accounts for 60% of attacks. Hackers were happy to borrow on other people’s names, foreign companies that now need to repay these loans.
As a result, if it was previously profitable to attack companies with the aim of stealing money from accounts, the work done by the regulator, and the development of protection systems reduce the attractiveness of financial companies, need too high competence and technical equipment. However, industry is the opposite. There hackers are just interested in data about clients, internal users and any information that relates to trade secrets.
Again, this leads to an increase in attacks on confidential data (from 12% to 20%). Personal data (32%), accounting data (20%) and medical information (9%) are also popular.
In general, 14% of attacks were directed at ordinary people, and 88% of attacks were through social engineering. Additionally, the ultimate goal in 66% of the cases — accounting and personal data.
Closing the chapter, I will give some more examples of the most resonant attacks of 2022 on organizations from the commercial sector:
— Lapsus$ group has hacked a number of large IT companies. It was first attacked by Okta, which develops solutions for account and access management, including multi-factor authentication support. Nvidia’s GPU developer was then attacked, resulting in the theft of 1 TB of data, including video card driver source code and software signing certificates. The stolen Nvidia certificates were used to distribute malware. In March, criminals were able to hack Microsoft and Samsung by stealing the source code of some products.
— The Swiss airline company Swissport, which operates at 310 airports in 50 countries, has been attacked by an extortion program. The attack caused numerous flight delays and a 1.6 TB data leak.
— The attack on the telecommunications operator Vodafone in Portugal caused disruptions in service throughout the country, including in the operation of the 4G and 5G networks. Vodafone Portugal serves more than 4 million cellular subscribers.
— In October, a cyber-attack on Supeo, an IT service provider for the largest Danish railway company, stopped trains for several hours. Supeo provides a solution that machinists use to access critical information — work data on tracks and speed limits. During the attack, the provider shut down its servers, causing the application to malfunction, and the drivers were forced to stop the trains. After the restoration of train traffic, the next day did not go on schedule.
— In March, Toyota suspended 14 factories in Japan for a day due to a cyber-attack on Kojima Industries, a component supplier. The cyber-attack also affected other Japanese car manufacturers — Hino and Daihatsu Motors.
— In the second quarter, a major attack occurred on three Iranian steel mills, disrupting technological processes, and in one of the factories, the attackers managed to bring down a liquid iron bucket and cause a fire.
Chapter 5. About Technology
Cloud computing
One of the most sought-after technologies for digitalization and digital transformation are cloud computing, storage and services. Accordingly, the focus in the IS organization is increasingly shifting to the responsibility of providers. Here you need to look from two angles:
— major cloud service and infrastructure providers;
— local startups and small providers.
As for the first, everything is fine here: the major providers realize that they will attack, and therefore will take measures. Forewarned means armed. Additionally, in general, cloud services of large providers are developed on the principle of “all enemies around”, plus they have competent specialists in IS. Such centralization also allows fewer professionals to protect more data.
However, relative to startups and small providers are getting sadder. They don’t have the resources, and they’re likely to lose most of their money clients. The same applies to local data centers and IT services that develop within industrial companies. They are generally unable to provide the necessary level of protection. Or, as they said earlier, they just begin to go into a blind defense, and for business loses all sense of such cloud services, they are simply impossible to use. At the same time, the number of malware for Linux is growing.
The fact that almost 40% of all vulnerabilities identified and closed in 2021 with the help of PT researchers have a high level of danger also makes you wonder. Most importantly, 12.5% of all vulnerabilities have been identified in the software designed to provide protection against hacker attacks. Additionally, despite all the current situation and sanctions, the guys from PT comply with the responsible disclosure policy regarding the found vulnerabilities, i.e. inform the developers about all found vulnerabilities before they are published in the public domain.
Mobile applications
The second area that is developing along with digitalization is mobile applications: for customers and loyalty programs, for employees, mobile handlers, fixation of dangerous events, public services. Any larger organization has its own application.
At the same time, according to PT, the most popular vulnerability of mobile applications is storing user data in an open (or easily reversible) form. There was also a situation where important data was stored in public directories. Additionally, the overall share of deficiencies associated with unsafe data storage was more than 33% of all vulnerabilities found. That is, what hackers are interested in, and is one of the most frequent problems.
Experts of PT in 2022 conducted a study of 25 pairs of applications (Android — iOS). Almost everyone had problems with data storage. One of the key reasons is the excessive confidence of developers in system protection mechanisms at the level of the operating system, ignoring multi-level protection.
The largest share of vulnerabilities (14%) was in the public storage of user data. The second place was divided by vulnerabilities related to checking the integrity of applications and storing confidential information in the code (9%).
Additionally, almost every application has at least one of the following flaws:
— no detection of operating system hacking (root on Android and jailbreak on iOS);
— lack of integrity control of executable files;
— no obfuscation (code entanglement).
Android and iOS: who is safer?
Android apps have always been considered a good target for hackers: open system, wide options, easy to leave a hole in the app. With iOS it has always been the other way around: developers have little opportunity to make a mistake and leave the unnecessary “doors” open. Additionally, there was a paradigm — we buy for TOPs devices on iOS, and they are protected. However, now there is a change in this trend. Google is increasingly restricting applications, forcing developers to specify the necessary functionality. Additionally, according to recent news, Android 14 will completely block the ability to install legacy apps. And both through the application store and through self-downloading installation files. In iOS, by contrast, new ways of interacting with the operating system and with each other are becoming available to applications. In general, the boundary between platforms is blurred, and using iOS devices for TOPs in the hope of absolute security becomes too risky an undertaking.
There again, social engineering
The key problem is the development of fake apps, external clones of official banks, stores and special applications. The removal of many companies’ mobile apps from official Android and iOS stores contributed to this, forcing users to search for them on other platforms and activate the installation from unknown sources on the devices themselves. The attackers take advantage of this: create fake clones, place them on various sites, collect the necessary data and then launch attacks on people and organizations, including by breaking into private offices.
Additionally, given that most people use personal gadgets for work tasks, we get another variation on the attack on the supply chain — the company can attack through employees and randomly and purposefully.
One practical example is the installation of SSL certificates. When connecting to an untrusted Wi-Fi network, the user is shown a fake captive portal and offered to install an SSL certificate on the device. After that, the attacker can intercept all traffic from the user’s smartphone.
Artificial intelligence
If we talk about using artificial intelligence (hereinafter — AI) in attacks, we can distinguish three key scenarios.
The first and most dangerous, but not yet feasible, is the creation of an autonomous neural network that analyzes the IT infrastructure itself, collects data, searches for vulnerabilities, attacks and contagion, encrypts data, and steals confidential information.
The second is to use AI as a support tool and to delegate specific tasks to it. For example, creating diphonics and voice simulations, conducting perimeter analysis and vulnerability search.
Additionally, the third scenario is that the neural networks are exposed in order to cause an error, to provoke an incorrect action.
Video, voice and biometrics switches
I think everyone has heard about the so-called deepfakes — a video where the face of the right person was exposed, his facial expressions repeated, and it is quite difficult to distinguish such a fake. I want to mention the fake voice separately. A few years ago, to fake your voice, you had to provide a neural network with one or two hours of recording of your speech. About two years ago, that number dropped to a few minutes. Well, in 2023, Microsoft introduced a neural network, which is three seconds long enough for a fake. Plus, there are tools that you can use to change your voice online.
Additionally, if in 2018 all this was more fun, then in 2021 became an active tool for hackers. For example, in January 2021, the attackers made a video with the help of a deepfake, where the founder of Dbrain invited everyone to the workshop and suggested to go to a link that is not related to his company. The purpose of the scammers was to lure new customers to the blockchain platform.
In March 2021, news of the deception of China’s state system, which accepted and processed biometric-certified tax documents, was reported. The app ran the camera on the phone and recorded video to confirm identity. The fraudsters in turn found photos of potential victims and with the help of AI turned them into videos. It should be noted that fraudsters approached the task in a complex way. They knew which smartphones had the necessary hardware vulnerabilities, that is, where you could run the prepared video without turning on the front camera. The damage amounted to $76.2 million. After the incident, China considered protecting personal data and introduced a draft law proposing penalties for such violations and personal data leaks of up to $8 million or 5% of the company’s annual income.
Another example from the UAE. The hackers faked the company director’s voice and forced a bank employee to transfer the money to fraudulent accounts, convincing him that it was the firm’s new accounts.
In Russia, hackers also do not lag. Surely you have already called representatives of “security” banks or just with some questionable promotions. Therefore, in April 2021, there was an incident when intruders called the victims, recorded their voice, and then tried to use these records to take credit in banks. Therefore, if you have doubts about who is calling you, it is better not to have a dialogue at all. Even if the number is trustworthy. I mean, it’s pretty easy to switch phones now. Personally, I’ve had this happen before: the number is identified as my bank number, but as it turns out, it was just frauds.
At the same time, there is no escape from biometrics. She came into our life completely. In the spring of 2021, news began to appear in Russia about the possible permission to donate biometrics through mobile applications. Additionally, in the Moscow subway, they introduced face recognition. The State has already adopted a law on the establishment of a public biometric data system. The use of biometrics will be possible not only in the subway, but almost in any store.
In addition, there are data leaks. Everyone already knows about the scandalous leaks from Yandex, we previously discussed the cracking of state databases, but in addition, according to the company DLBI, in 2022, 75% of the data of all Russians leaked. As a result, leaks affected 99.8 million unique e-mail addresses and 109.7 million phone numbers. I can tell by myself that changing the password and using it as a standard on most services leads to the fact that after 1—2 months it is detected as compromised.
As a result, laws and fines are tightened by the State. Additionally, even if you are a small company that creates an IT solution, it is better to think about it beforehand.
ChatGPT
It is impossible to bypass here and the main news of the beginning of 2023 — the neuronetwork ChatGPT. Hackers actively use it to create viruses. Based on a huge database, the ShatGPT neural network can generate virtually any material, including software code, without using the Internet.
The experts from Check Point Research published a report in which they described how hackers use ChatGPT to write malicious code and phishing emails — some of these people have little or no experience in programming. The experts demonstrated two scripts (short action algorithms), one of which, with a small revision, can be turned into a ransomware that encrypts data, and the other searches files of a given type for theft.
AI was also able to compose a convincing phishing letter that suggested opening an Excel file that AI had previously infected. After several attempts ChatGPT also wrote the embedded VBA macro.
AI can automatically collect information from open sources on certain topics, and even on specific people, if their personal data is known. As a result, such “dossiers” on a person can increase the effectiveness of phishing attacks, especially if it is collected from database leaks.
It is also important to consider that ChatGPT and other solutions collect and store user requests. Additionally, this is the way to data leakage.
Another experiment — requests for modification of the result allowed to create polymorphic malware. It does not show its malicious activity during disk storage and leaves no traces in memory, making it very difficult to detect such code.
Blockchain
Blockchain is another technology that everyone is hearing: cryptocurrencies, NFT, smart contracts. Additionally, because it’s connected to money, it’s being actively studied by researchers. Therefore, there are no vulnerabilities. Everything that’s been found lately is unique. True, this does not prevent losses: for 2021 worldwide, they exceeded 1.3 billion dollars, and in 2020 this value was at the level of 800 million dollars. In 2022, losses were estimated at $3.8 billion.
An example is the theft of money from the Ronin blockchain system. The attackers managed to withdraw almost $620 million in Ethereum and USDC tokens. Other breakdowns include FTX ($650 million), BSC Token Hub ($566 million), Wormhole ($326 million) and Nomad ($190 million)
All security concerns of decentralized finance are now divided into three categories.
1. Lack of technology
There is a lack of specialized tools in the world for servicing smart contracts and quick search of vulnerabilities in code. The language in which smart contracts are written is vulnerable at the system level. Now, of course, new blockchain technologies are emerging, languages in which these bugs are fixed at the architecture level, but they are not yet as popular and common. There are tools to navigate, but every crutch is a possible vulnerability. For example, the most famous hack in 2021 was wearing just such a crutch, when hackers stole more than $300 million and then returned them.
2. Mathematical, concerning errors in the logic of smart contracts, in particular related to attacks “instant loans”.
Blockchain allows you to become a real millionaire for 10 seconds: an attacker can borrow any amount of money, use them for their own interests, for example, affect other smart contracts, scroll them on the stock market. It is necessary to return them in the same block, that is, within 10 seconds. This scheme is called instant credit or flash loan attacks.
Additionally, it was errors in smart contract logic that were most often used by intruders — in 78% of attacks. In most cases, it is for such instant credits.
3. Related to users
Here again we are talking about phishing. In addition to human negligence, the problem of unprocessed UX-design is added. Therefore, the interface, for example, is unfriendly. In general, techs design for the advanced. Hackers create credible sites, exploit vulnerabilities and phishing rules are all the same as in other directions. As a result, the damage from such attacks worldwide in 2021 reached 14 billion dollars. Additionally, most importantly, unlike hacking smart contracts, such attacks are easily feasible.
Practical example — fraud with Airdrop (airdrop): users received emails about the free distribution of cryptocurrencies, tokens or NFT. Donating assets for specific user actions is really popular with cryptocurrency startups at startup. However, attackers, disguised as free NFT tokens and virtual collectible items, send malware.
Is it possible to prevent the vault from being breached? On the one hand, when we talk about blockchain, we talk about anonymity because the account itself is an alphanumeric address. However, it is still possible to trace where the funds came from to balance a particular wallet. As a result, it is possible to identify the chain up to a centralized cryptographic exchange, such as Binance, where, in addition to using a real bank card, you need to go through a thorough verification of identity documents, and even confirmed utility bills. Therefore, hackers do not use Binance, referring to specialized services that allow to hide the history of receiving money. In this case, however, additional services are now available to determine whether the money associated with the transaction passed through the Tornado Cash. With these features, the transaction is blocked.
Chapter 6. How companies are attacked
As before, hackers use a combination of vulnerabilities and social engineering. For example, first, research of a person and/or a company, a division, and then through phishing and psychological manipulation, provoke necessary action or disclosure of information. This can be the correct password or go to a special link, or, in the case of bank fraudsters, proven CVC code. The important thing is it works.
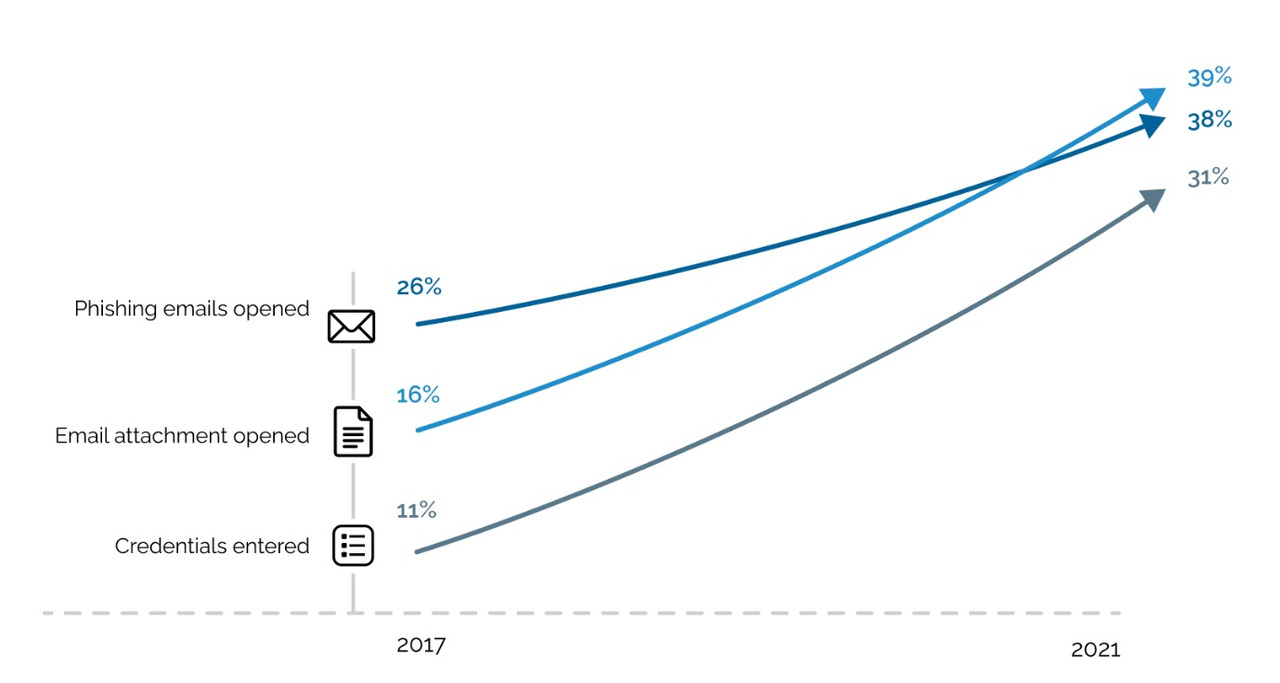
I remind you of statistics. During the projects in 2017, 26% of employees went to the link in the phishing letter, 16% launched a file, and credentials were entered into fake authentication forms in 11% of cases. By the end of 2021, there are no improvements: 38% of employees go through the links in phishing emails, 31% enter the credentials, and malicious attachment can be launched in 39% of cases.
In terms of numbers, social engineering in 2022 among all successful attacks on companies — 43%, and in 89% of cases it was emails. Malware was used in 54% of attacks. That is, attacks become hybrid.
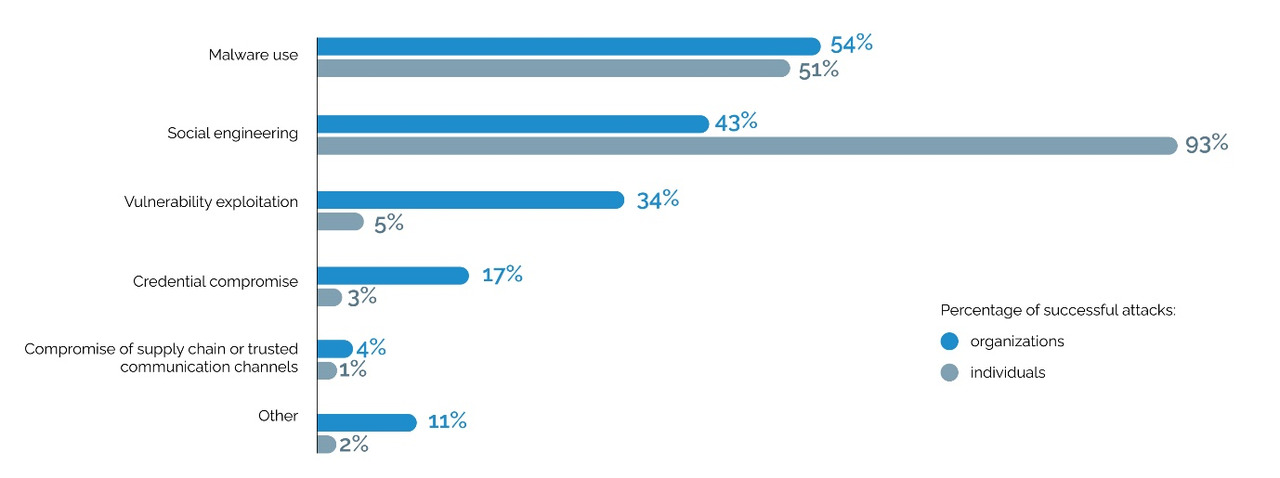
Additionally, more than 66% of all malware — encryptors. Plus, the use of vipers — programs that delete data is growing actively. The growth here was 175% against 2021. For industrial companies, the share of coders all 78%. After all, why try to understand processes, technologies, when you can just and easily run one program and just deprive you of information. Additionally, then, if we can get it out, we can sell it.
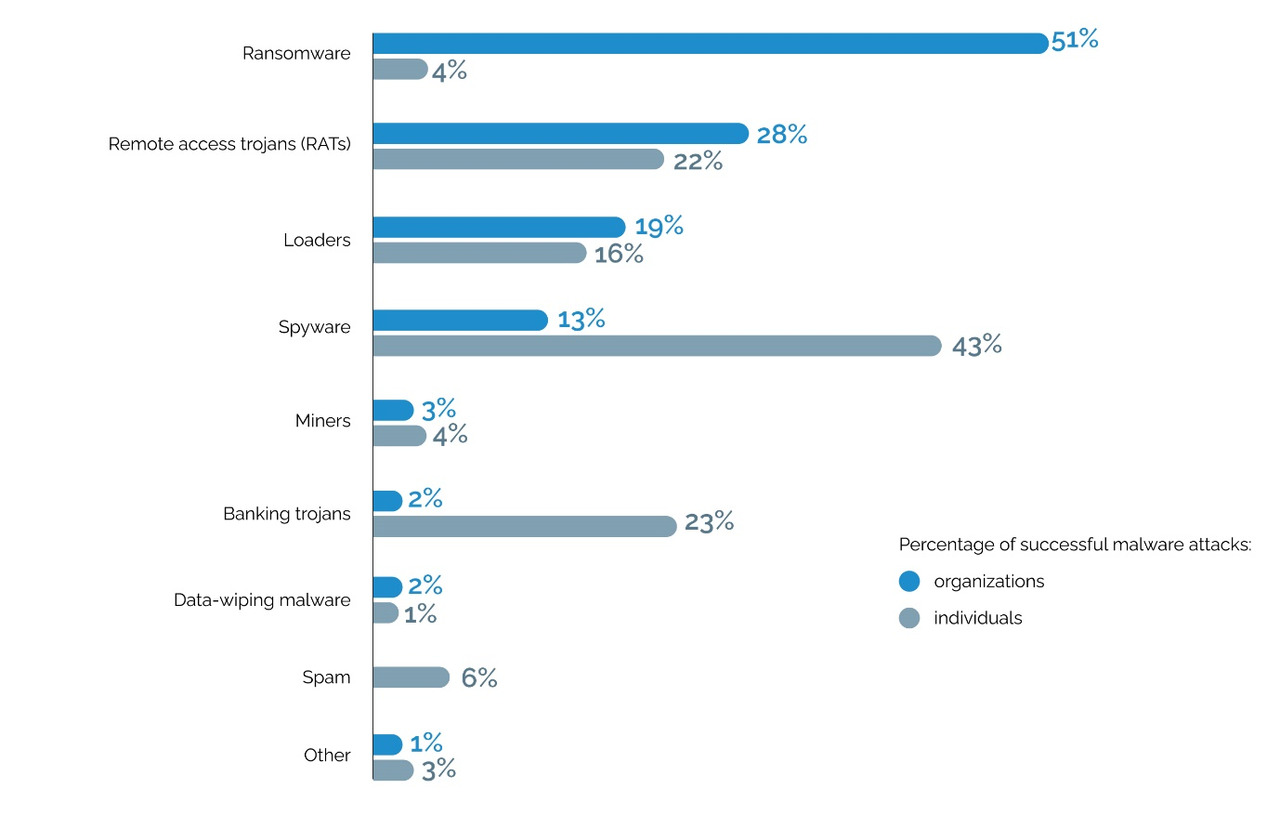
Additionally, hackers have a reputation for vulnerability: not only is the number of software growing, its complexity, vulnerabilities do not close for years, but also the developer does not know about all of them. In terms of statistics, an average of 31,066 vulnerabilities to a large organization are identified in one pilot. Of these, 57% are critical and dangerous. It is necessary to eliminate immediately 3%, that is about 900, which is also a lot.
Now consider the typical attack algorithm.
Step 1. Traversing the network perimeter
The first step for the attacker is to overcome the network perimeter, that is, the external circuit. Thus, in their projects PT specialists in the second half of 2020 — the first half of 2021 were able to overcome the network perimeter in 93% of cases even without the use of social engineering. The main method of penetration is the collection of credentials. This is primarily due to staff setting simple passwords, even for administrator accounts. The compilation of accounting data allowed crossing the external perimeter in 71% of the projects.
At the same time, outdated versions of software and unsafe protocols make it possible to exploit already known vulnerabilities. Thus, PT specialists, when tested by an external attacker, were able to use vulnerabilities to penetrate 60% of projects, and 43% — vulnerability was in the web application code. Among the vulnerabilities were:
— “Remote execution of arbitrary code” in the Microsoft Exchange server accessible from the Internet;
— “Reading Arbitrary Files”
— “Disclosure of information” in the web interface of control of Cisco ASA devices;
— “Remote execution of arbitrary code” in Microsoft SharePoint;
— “Remote execution of OS commands” in Citrix NetScaler software;
— In almost every company there is a way to penetrate the local network through web applications.
The average number of simultaneous directions for penetration into the internal network per company — 3, the maximum — 19.
Бесплатный фрагмент закончился.
Купите книгу, чтобы продолжить чтение.